In In late 2023, the Nigerian Association of Resident Doctors disclosed that over 1,400 of its members were preparing to depart the country for better opportunities in the United Kingdom and the United States before the year ends.
This did not include the 900 doctors who had already left the country between January and September, as stated by the NARD president, Dr. Dele Abdullahi.
Speaking with The PUNCH, he linked the mass exodus to the poor working conditions in the country.
“We have a continual loss that has resulted in a chronic scarcity of manpower within the healthcare systems. The ongoing loss is now causing issues.
“The problem is not just what happens at the end of the year but what is continuously happening. We have ongoing data and we are consistently receiving this information.”
In the report, a former president of the Nigerian Medical Association, Prof. Innocent Ujah, referred to the ongoing migration of medical doctors as the second peak of doctors’ mass departure after the significant exit of medical practitioners from the country in the 1990s.
This continuous departure adds to the challenges already faced by the struggling health sector in the country.
Aside from inadequate pay and working conditions for the doctors, other reasons that have contributed to the departure are poor coordination of the health care system, underfunded and run-down health facilities – where they are available – inadequate funding as well as corruption hindering any form of progress in the health sector.
While these distressing factors have led to the departure of many doctors, the few remaining are left to shoulder the burden of tending to the healthcare needs of a country with no less than 200 million citizens.
The World Health Organization suggests 1:600 as the standard ratio of doctor to patient, whereas, as of 2022, the NMA reported the ratio in the country was 1:5,000.
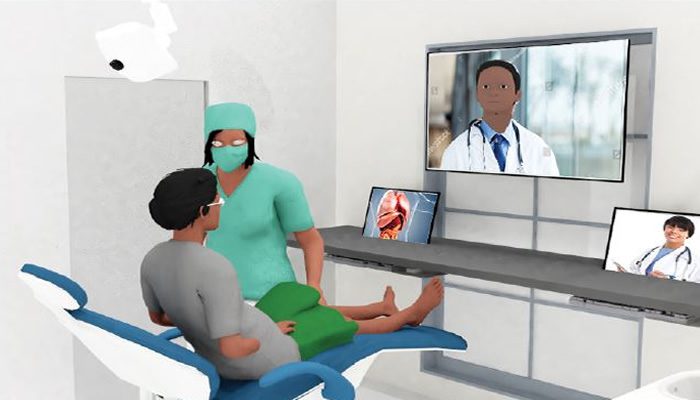
Telemedicine and its role in healthcare
As the burden on the limited medical professionals in the Nigerian health system worsens, it has become necessary for health workers to diversify and incorporate the use of modern technology to reach the large number of patients who visit the hospitals daily seeking healthcare, hence, the need for telemedicine.
As technology progresses, its impact on healthcare is evident. Telemedicine is one of the growing aspects of healthcare with numerous apps providing healthcare services that eliminate the need to physically visit a doctor, which is especially helpful in a country like Nigeria where citizens struggle with access to healthcare.
Telemedicine, as explained by Medical News Today, is a term that encompasses the use of technology to provide clinical care from a distance. It ensures that a person receives healthcare when necessary, particularly for those with limited access to care.
“Telemedicine uses electronic and telecommunication technology to facilitate the exchange of medical information, even when a person and their doctor are not in the same room.
“It can be as basic as sending medical care through text messages or as advanced as performing surgery remotely,” it stated.
The medical education site stated that telemedicine enables a person to consult a doctor about non-urgent situations that do not require an in-person visit. Some examples of telemedicine are remote consultations, telediagnosis, and telemonitoring.
Other types of telemedicine include platforms that offer live chat with medical experts, text messaging services, audio advisory, and visual medical services with the help of AI.
It is said that in the US, 76 percent of hospitals use video conferencing or other technology to connect with people at a distance.
As a country that is not yet advanced in merging healthcare and technology, with the current issues faced by both patients and doctors, experts have said that telemedicine can bridge the gap to make healthcare more accessible and reduce unnecessary hospital visits in Nigeria.
A professor of Medicine and Endocrinology at the College of Medicine, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomoso, Michael Olamoyegun, stated that now is the perfect time to introduce telemedicine to mainstream medical care in Nigeria.
However, he noted that Nigerians have been participating in telemedicine over the years without realizing.
Advantages of telemedicine in Nigeria
“There is a great need for the introduction of telemedicine. We are talking about managing patients from a distance,” Olamoyegun, who is also a consultant endocrinologist, said.
He said, “If there has been any time for the introduction of telemedicine in Nigerian healthcare, this is the time. If you look at the number of medical practitioners, they are grossly inadequate and the few hands available are leaving the country so the number keeps depleting.
“Most specialities have limited specialists that can manage patients. Apart from that, most specialists in different areas are concentrated in cities with little or none in remote places, and yet these people also need to benefit from the expertise of the specialists. So, there is a need to use telemedicine.”
Olamoyegun added that introducing the use of telemedicine was necessary to also help those who reside in remote villages to have access to quality healthcare services and providers just as those in the cities do.
The use of telemedicine will surely enhance healthcare service penetration and delivery in the nation, he argued.
Referring to the benefit of its integration in hospitals, another medical expert, Dr Olusina Ajidahun, said, “It is not news there has been a massive exodus of doctors as a result of that, the doctor-to-patient ratio is very reduced so telemedicine can bring down that.”
“Another is that if you talk to Nigerians and ask them why they don’t like going to the hospital, they will tell you that they don’t like the wait time in the hospitals and that telemedicine decentralises all of that.”
Ajidahun pointed out that telemedicine was not just for doctors alone, but also includes accessing the services of other healthcare providers like dieticians, physiotherapists, and others.
Furthermore, telemedicine falls within the category of the use of technology in healthcare which includes using artificial intelligence and other technological innovations for medical issues that can be solved with technology.
Additionally, practicing telemedicine can be a way for doctors to earn extra money, he explained. He also believes that telemedicine will significantly reduce the chances of patients encountering problems when they visit unqualified doctors.
“I believe that if all of these factors are considered, telemedicine is something we should welcome,” he added.
Chuks Chibundu, the CEO of DoctorCare247, a digital healthcare platform that enables real-time remote consultation and non-invasive diagnosis between patients and doctors, pointed out that using telemedicine in the Nigerian healthcare system is crucial for addressing the gaps left by poor public health care.
According to him, telemedicine fills the gap in the availability of medical experts, provides patients with numerous options to choose from, and is more cost-effective than a traditional hospital visit.
“Telemedicine closes the distance gap. Another benefit is the convenience of access. Visiting a public hospital is often not convenient, and that is where telemedicine comes in,” he said.
“When you consider all these gaps, you'll see telemedicine providing an alternative. It's not a complete alternative, but an option for quality health delivery where you can consult a doctor from the comfort of your location,” he pointed out.
Challenges to accepting telemedicine
Despite the increasing need to incorporate telemedicine into mainstream healthcare, it may face some difficulties.
One of the reasons telemedicine is not progressing in Nigeria is because many people do not comprehend it, according to Ajidahun.
He admitted that although the acceptance was still slow, and many people are traditional in their thinking, its acceptance was primarily among the educated and younger generation.
He further stated that another reason for the slow embrace is patients' fear of being deceived.
“Due to the fear of being deceived, some people still prefer visiting the hospital. Additionally, some people are averse to paying for services, so they question why they should have to pay for a phone consultation instead of going to the hospital,” he pointed out.
Chibundu added that the slow acceptance is due to the level of understanding among citizens.
“There is a misunderstanding here. People believe that because it involves technology, it is advanced, but it's not. It's a simple technology. It essentially combines the power of information and telecommunication.
“So, it is taking time to be adopted due to the lack of understanding. What we need to do is educate and promote it,” he said.
Role of government
On December 12, President Bola Tinubu reassured Nigerians that his administration was committed to prioritising and improving Nigeria’s health sector through massive investments and an increased allocation of funds in the proposed 2024 budget.
In the N27.5tn budget estimates for the 2024 fiscal year, the health sector received N1.33tn (a mere 4.8 percent of the budget, which is still below the 15 percent target set by African leaders in the Abuja Declaration).
1.07 trillion naira was designated for regular spending in the Federal Ministry of Health and its agencies, 137.21 billion naira for Gavi/ immunisation funds, which includes funding that matches what donors give, and 125.74 billion naira for transferring to the Basic Healthcare Provision Fund.
However, Ajidahun suggested that the government should support technological advances in healthcare, especially through partnerships between the public and private sectors, as well as through funding.
“I believe that a partnership between the government and private companies would be very useful in addressing healthcare issues.
“This can generate more income for both the government and hospitals. It will also decrease the number of people visiting hospitals, as more people will use technology,” he said.
Prof Olamoyegun emphasized the critical role of the government in promoting the service.
“One way for the government to begin is to promote and raise awareness about this. Let people know that there are many ways to manage patients without having to go to the hospital,” he said.
Network expansion and telemedicine
Data analytics by Datareportal indicated that as of the beginning of 2023, there were 122.5 million Internet users in Nigeria in January 2023 while the Internet penetration rate was 55.4 percent of the total population for the same period.
This implies that for telemedicine to be more widely available in the country, more people need to adopt technology. However, this could be difficult due to the state of network service in the country.
Additionally, the Nigerian Communications Commission recently blocked 40 million telephone lines for not linking their number to their national identity numbers, which affected service provision.
Therefore, for telemedicine to be integrated into Nigerian healthcare, collaboration is needed among information, medicine, and network production to reach every part of the country for easy access to healthcare.